|
|
Responsible stewardship for now ... and the futureThe Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant is located along the Carlsbad coastline, and adjacent to one of North County San Diego’s most precious natural resources - the Agua Hedionda Lagoon.
|

The Agua Hedionda Lagoon is a 400-acre man-made, shallow coastal embayment teeming with marine life. The lagoon hosts four main habitats; the Marshlands, where the saltwater lagoon meets with freshwater creeks; the Upland Plant Communities; the Intertidal Mudflats, which are location along edges of the lagoon; and the Subtidal habitat, which is primarily underwater. Each of these habitats support a thriving ecosystem, which includes 70 species of fish, 20 species of amphibians and reptiles, 24 species of mammals, 192 species of birds, 175 species of invertebrates and 100 species of plants.
The lagoon is also home to an array of recreational and educational activities, and environmental research. The lagoon supports a thriving marine ecosystem and is home to the Hubbs-SeaWorld fish hatchery, the Carlsbad Aquafarm, YMCA Camp and the Lagoon Foundation's Discovery Center.
The lagoon is also home to an array of recreational and educational activities, and environmental research. The lagoon supports a thriving marine ecosystem and is home to the Hubbs-SeaWorld fish hatchery, the Carlsbad Aquafarm, YMCA Camp and the Lagoon Foundation's Discovery Center.
|
Poseidon Water will be dredging the Outer Basin of Agua Hedionda Lagoon to maintain the tidal flow thru the Lagoon and replenishing the sand on Carlsbad beaches. For more information see our AHL Dredge Frequently Asked Questions, Stakeholders Meeting Presentation, Stakeholders Invitation List and 2020/21 Dredge and Sand Deposition Plan. For more information and updates on the 2020/21 Dredging of Agua Hedionda Lagoon please contact us.
To learn more about the Agua Hedionda Lagoon, visit the Agua Hedionda Lagoon Foundation’s website at www.lagoon.aguahedionda.org. |
| Map of Agua Hedionda Lagoon | |
| File Size: | 5753 kb |
| File Type: | |
More than a water supply project, the desalination plant will preserve and enhance air quality and the environment.
- To include Wildfire Reforestation by planting 5,000 trees in areas damaged by local wildfires.
- View our final Marine Life Mitigation Plan and final Energy Minimization and Green House Gas Reduction Plan (appendices not included).
Mitigation
 Mitigation Site Map - click to download a larger PDF version.
Mitigation Site Map - click to download a larger PDF version.
The Otay River Estuary Restoration Project (ORERP) is a partnership between the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or Service) and Poseidon Resources (Poseidon) to create, restore, and enhance coastal wetlands to benefit native fish, wildlife, and plant species, and to provide habitat for migratory seabirds and shorebirds and salt marsh–dependent species within the South San Diego Bay Unit of the San Diego Bay National Wildlife Refuge (San Diego Bay NWR).
The ORERP implements the habitat restoration objectives of the San Diego Bay NWR Comprehensive Conservation Plan (CCP) (USFWS 2006), and fulfills the applicable terms and conditions of the permits issued to Poseidon by the California Coastal Commission (Commission) and San Diego Regional Water Quality Control Board (Regional Board) for the Carlsbad Desalination Project. The partnership between the Service and Poseidon provides public benefits by restoring coastal wetlands and wildlife habitats within the San Diego Bay NWR, and allows Poseidon to meet its mitigation requirements for the Carlsbad Desalination Project.
The ORERP proposes to restore approximately 125 acres of coastal wetlands and associated uplands at two locations on the San Diego BayNational Wildlife Refuge (San Diego County, California), including a 33.5-acre portion of the Otay River floodplain, and a 91-acre active solar salt pond(Pond 15). To achieve elevations appropriate for supporting sub-tidal and intertidal wetlands within the Otay River Floodplain Site, the action alternatives propose the excavation of 320,000 to 370,000 cubic yards of material or which 260,000 to 310,000 cubic yards would transported to the Pond15 Site to be beneficially used to restore coastal wetlands within the pond.The remaining 30,000 to 40,000 cubic yards of material would be stockpiled on the Refuge for future beneficial use. View the Draft Environmental Impact Study (DEIS) for the proposed project.
The ORERP implements the habitat restoration objectives of the San Diego Bay NWR Comprehensive Conservation Plan (CCP) (USFWS 2006), and fulfills the applicable terms and conditions of the permits issued to Poseidon by the California Coastal Commission (Commission) and San Diego Regional Water Quality Control Board (Regional Board) for the Carlsbad Desalination Project. The partnership between the Service and Poseidon provides public benefits by restoring coastal wetlands and wildlife habitats within the San Diego Bay NWR, and allows Poseidon to meet its mitigation requirements for the Carlsbad Desalination Project.
The ORERP proposes to restore approximately 125 acres of coastal wetlands and associated uplands at two locations on the San Diego BayNational Wildlife Refuge (San Diego County, California), including a 33.5-acre portion of the Otay River floodplain, and a 91-acre active solar salt pond(Pond 15). To achieve elevations appropriate for supporting sub-tidal and intertidal wetlands within the Otay River Floodplain Site, the action alternatives propose the excavation of 320,000 to 370,000 cubic yards of material or which 260,000 to 310,000 cubic yards would transported to the Pond15 Site to be beneficially used to restore coastal wetlands within the pond.The remaining 30,000 to 40,000 cubic yards of material would be stockpiled on the Refuge for future beneficial use. View the Draft Environmental Impact Study (DEIS) for the proposed project.
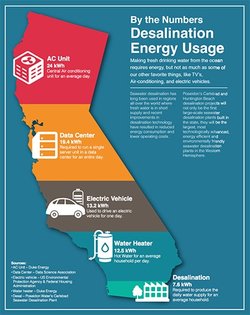
Energy efficiencySeawater desalination has long been used in regions all over the world where fresh water is in short supply. Today, there are more than 15,000 desalination plants worldwide in 150 countries, producing more than 18 billion gallons of fresh drinking water per day. An estimated 70 million people around the world rely on desalinated water for their daily water needs.
Recent advancements in reverse osmosis desalination technology make this method of securing fresh drinking water increasingly cost effective and, therefore, an even more viable option for ensuring water supply reliability. Coupled with other improvements in desalination technology, these advances have resulted in reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs. This technology is being used at the Carlsbad Desalination Plant to make it the most energy-efficient desalination plant in the nation. The Carlsbad Desalination Plant utilizes state-of-the-art pressure exchanger devices made by Energy Recovery, Inc. Because the device consumes no electricity and recycles otherwise lost energy, much like a hybrid car, the overall energy consumption of the reverse osmosis process is reduced by nearly 46 percent. This technology allows the desalination plant to save an estimated 146 million kilowatt-hours of energy per year, the equivalent of $12 million per year. As a result, they reduce carbon emissions by 42,000 metric tons annually – roughly equivalent to the annual greenhouse gas emissions from 9,000 passenger vehicles – by recycling the pressure from the reverse osmosis process. |
Energy recovery system.
|
© 2017 Carlsbad Desalination Project : 5780 Fleet Street, Suite 140, Carlsbad, CA 92008 | (760) 655-3900
All Rights Reserved. Contact | Login.
All Rights Reserved. Contact | Login.